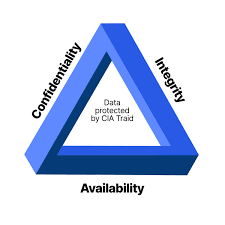
Information Security (InfoSec) is a broad field concerned with the protection of information from unauthorized access, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. It involves a combination of policies, processes, and technologies designed to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA) of data.
Core Principles of Information Security:
1 .Confidentiality: Ensures that information is accessible only to those authorized to have access. It involves measures like encryption, access controls, and authentication to protect sensitive data from being accessed by unauthorized individuals.
- Integrity: Ensures the accuracy and completeness of data. This principle involves protecting information from being altered in unauthorized ways. Mechanisms like hashing, checksums, and version control are used to maintain data integrity.
- Availability: Ensures that information and resources are accessible to authorized users when needed. This involves ensuring that systems are reliable and that there are measures in place to recover from failures or disruptions, such as backups and disaster recovery plans

Key Components of Information Security:
1) Risk Management: Identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks to information assets, followed by coordinated efforts to minimize, monitor, and control the impact of these risks.
2)Access Control: Mechanisms that limit who can view or use resources in a computing environment. This includes user authentication (verifying the identity of a user) and authorization (ensuring the user has permission to access specific data).
3)Cryptography:The use of mathematical techniques to secure information, ensuring that only those with the correct key can access the data. This includes encryption (scrambling data into unreadable formats) and decryption (converting it back into its original format).
4)Incident Response: A structured approach to handling security breaches or cyber attacks. The goal is to manage the incident in a way that limits damage and reduces recovery time and costs.
5)Security Policies: Formalized rules and guidelines that govern how information and resources are to be used and protected. These policies provide a framework for implementing and managing security measures.
Common Threats in Information Security:
-Malware: Malicious software designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems. Examples include viruses, worms, ransomware, and spyware.
- Phishing: A method of tricking individuals into divulging sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card numbers, often by pretending to be a legitimate entity.
- Insider Threats:Threats that come from within the organization, such as employees who intentionally or unintentionally compromise information security.
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: Attacks aimed at making a system or network unavailable to its intended users by overwhelming it with traffic or sending it information that causes it to crash.
Importance of Information Security:
- Protecting Sensitive Data: Organisations often deal with sensitive information, such as financial records, personal data, and intellectual property. InfoSec ensures this data is protected from theft and misuse.
- Compliance: Many industries are subject to regulations that require certain levels of information security. Compliance with laws like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS is essential to avoid legal penalties and maintain trust with customers.
- Business Continuity: Information security helps ensure that businesses can continue to operate even in the face of cyber attacks or other disruptions. This includes having disaster recovery plans and backup systems in place.
- Reputation Management: A security breach can severely damage an organization’s reputation. By maintaining strong security practices, companies can protect their reputation and maintain customer trust.
- Information Security Management Systems (ISMS):
- An ISMS is a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information so that it remains secure. It includes people, processes, and IT systems by applying a risk management process. ISO/IEC 27001 is one of the most popular standards for establishing an ISMS.
- Emerging Trends in Information Security:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Security: AI is increasingly being used to detect and respond to threats faster than humans can.
- Zero Trust Architecture: A security concept that requires all users, whether inside or outside the organization’s network, to be authenticated, authorized, and continuously validated before being granted access to applications and data.
- Cloud Security:As more organizations move to cloud computing, ensuring the security of data stored in the cloud has become a significant focus.
In summary, Information Security is essential for protecting data and systems from a wide range of threats. It involves a comprehensive approach that includes technical solutions, policies, and ongoing risk management to safeguard the information critical to both individuals and organizations.



