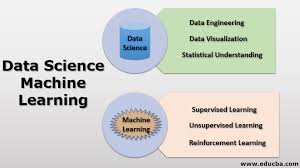
In data science, machine learning is used to analyze and interpret large datasets to extract valuable insights and make data-driven decisions. It involves training algorithms on historical data to identify patterns and trends, which can then be used to make predictions or classify new data.
Key applications include:
1. Predictive Analytics – Forecasting future trends based on past data.
2. Classification- Categorizing data into predefined classes (e.g., spam detection in emails).
3. Clustering- Grouping similar data points together (e.g., customer segmentation).
4. Recommendation Systems – Suggesting products or content based on user behavior (e.g., Netflix recommendations).
5. Anomaly Detection – Identifying unusual data points that may indicate fraud or errors.
Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are related but distinct concepts:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- Definition: AI is a broad field focused on creating systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as reasoning, problem-solving, and learning.
- Scope: Includes various techniques and approaches like rule-based systems, knowledge representation, and optimization, beyond just machine learning.
- Objective: To create intelligent agents capable of understanding and interacting with the world in a human-like manner.
2. Machine Learning (ML):
- Definition: ML is a subset of AI that specifically focuses on the development of algorithms and models that enable computers to learn from and make predictions based on data.
- Scope: Primarily concerned with data-driven methods and statistical models to improve performance on a given task over time without being explicitly programmed.
- Objective: To develop systems that can automatically improve their performance with experience and data.
In summary, AI encompasses a wide range of technologies and approaches aimed at simulating human intelligence, while ML is a specific approach within AI that uses data and algorithms to enable systems to learn and make predictions.




