
 Computer vision plays a crucial role in data science, enabling machine to interpret, understand and make decisions from visual data. It acts as a bridge between the physical world and the digital realm, allowing data scientists to analyze images and videos to gain a deeper understanding of various phenomena.
Computer vision plays a crucial role in data science, enabling machine to interpret, understand and make decisions from visual data. It acts as a bridge between the physical world and the digital realm, allowing data scientists to analyze images and videos to gain a deeper understanding of various phenomena.
Computer Vision is a subfield of Deep Learning and Artificial Intelligence where humans teach computers to see and interpret the world around them.
Who is a Computer Vision Engineer?
A Computer Vision Engineer is a specialist who develops systems that enable computers to process and interpret visual data, much like how humans perceive the world through sight. This involves:
- Creating and fine-tuning algorithms that allow machines to identify and understand images and videos, making decisions based on what they “see.”
The work typically revolves around tasks such as:
- Image recognition
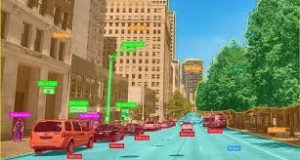
- Object detection
- Segmentation
- Pattern recognition
By leveraging advanced techniques in image processing and deep learning, Computer Vision Engineers bridge the gap between digital images and actionable insights, enabling applications ranging from autonomous vehicles to medical diagnostics.
Here’s a breakdown of computer vision’s roles in data science:
1. Expanding Data Sources:
-
- Computer vision expands the types of data available to data scientists beyond traditional tabular data. It allows them to incorporate images and videos into their analysis, creating richer and more comprehensive datasets.
-
- This is particularly important in fields like healthcare (medical imaging), manufacturing (quality control), agriculture (crop monitoring), and autonomous vehicles (object detection and navigation) where visual data is abundant.
2. Feature Extraction and Representation:
-
- Computer vision algorithms can automatically extract relevant features from images and videos, which can then be used as input for machine learning models. This eliminates the need for manual feature engineering, saving time and effort.
-
- For example, in image classification, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) can identify patterns and shapes within images to determine what objects are present.
3. Enhancing Data Analysis and Interpretation:
-
- By analyzing visual data, computer vision can help identify patterns, anomalies, and trends that might be missed by other methods.
-
- This can lead to more accurate predictions, improved decision-making, and a better understanding of complex systems.
4. Enabling Automation and Efficiency:
-
- Computer vision can automate tasks that would otherwise require manual human inspection or analysis, such as quality control in manufacturing or medical diagnosis.
-
- This automation can lead to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and faster processing times.
5. Complementing Other Data Science Techniques:
-
- Computer vision can be combined with other data science techniques, such as natural language processing (NLP), to create more powerful and comprehensive analysis pipelines.
-
- For example, combining image analysis with text analysis can help understand the context of visual data more effectively. Specific examples of computer vision applications in data science:
-
- Object detection and recognition: Identifying and locating objects within images (e.g., faces, cars, pedestrians).
-
- Image classification: Categorizing images based on their content (e.g., classifying images of cats, dogs, or birds).
-
- Image segmentation: Dividing an image into different regions based on object boundaries (e.g., separating different organs in a medical scan).
-
- Anomaly detection: Identifying unusual or unexpected patterns in visual data (e.g., detecting defects in manufactured products or unusual activity in surveillance footage).
-
- Facial recognition: Identifying and verifying individuals based on their facial features.
-
- Optical character recognition (OCR): Extracting text from images (e.g., scanning documents or license plates).
In conclusion, computer vision is an essential tool for data scientists, allowing them to unlock valuable insights from visual data and improve the accuracy, efficiency, and comprehensiveness of their analyses.
Last Update: June 24, 2025
